When diving into the world of statistics, you may come across terms like significance level and confidence coefficient. For someone starting out, these concepts can feel confusing, especially when trying to understand how they relate to each other. A common question that arises is, is significance level equal to confidence coefficient? While these terms are closely related, they are not the same. However, their relationship is crucial for interpreting statistical data correctly.
In this article, we will explain the significance level and confidence coefficient, explore their differences, and clarify their relationship in a way that is easy to grasp. By the end, you will understand how these terms are used in hypothesis testing and interval estimation, and why they are vital for sound statistical analysis.
Also Read: Lensestax.shop
What Is Significance Level?
The significance level, often denoted by the Greek letter α\alphaα, is a statistical threshold used in hypothesis testing. It defines the probability of rejecting the null hypothesis (H0H_0H0) when it is true. This type of error is called a Type I error, and the significance level helps control how often it occurs.
For example, if the significance level is set at 0.05, it means there is a 5% risk of incorrectly rejecting the null hypothesis. In other words, you are willing to accept a small chance of making a false positive error in your test results.
Common significance levels include:
- 0.05 (5%)
- 0.01 (1%)
- 0.10 (10%)
These levels are chosen based on the importance of avoiding errors in the specific context of the analysis. A smaller significance level, such as 0.01, is used in studies where errors have serious consequences, like medical research.
What Is Confidence Coefficient?
The confidence coefficient, on the other hand, represents the proportion of times that a statistical method is expected to produce accurate results. It is directly related to the confidence interval, which provides a range of values likely to contain the true population parameter.
The confidence coefficient is often expressed as a decimal, such as 0.95 or 0.99. This corresponds to the confidence level, which is the percentage equivalent. For example:
- A confidence coefficient of 0.95 means you are 95% confident that the interval contains the true value.
- A confidence coefficient of 0.99 means you are 99% confident in the results.
The confidence coefficient measures the reliability of a statistical estimate, making it an essential part of interval estimation.
Is Significance Level Equal to Confidence Coefficient?
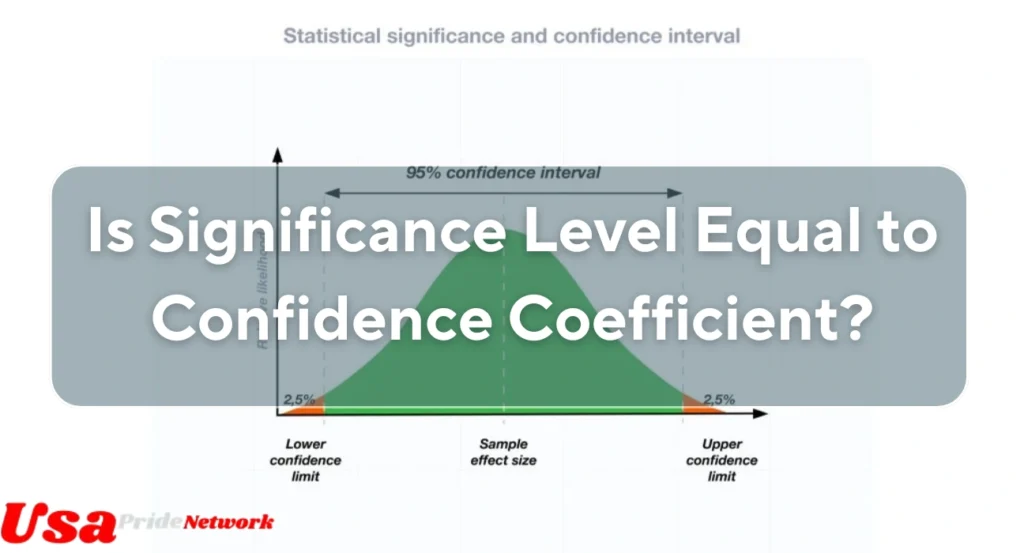
Now, let’s address the primary question: is significance level equal to confidence coefficient? The answer is no. These two terms are related but are not the same. They are, however, complementary to one another.
The relationship between significance level (α\alphaα) and confidence coefficient (1−α1 – \alpha1−α) is straightforward:
Confidence Coefficient=1−Significance Level\text{Confidence Coefficient} = 1 – \text{Significance Level}Confidence Coefficient=1−Significance LevelIs Significance Level Equal to Confidence Coefficient?
This means that if you know the significance level, you can calculate the confidence coefficient, and vice versa. For instance:
- If the significance level is 0.05, the confidence coefficient is 1−0.05=0.951 – 0.05 = 0.951−0.05=0.95, or 95%.
- If the significance level is 0.01, the confidence coefficient is 1−0.01=0.991 – 0.01 = 0.991−0.01=0.99, or 99%.
The complementary relationship helps statisticians balance the risk of Type I errors with the reliability of their estimates.
Hypothesis Testing and the Role of Significance Level
To fully grasp whether is significance level equal to confidence coefficient, it is important to understand their roles in hypothesis testing. The significance level (α\alphaα) determines the cutoff for deciding whether to reject the null hypothesis.
In hypothesis testing:
- You start with a null hypothesis (H0H_0H0), which assumes no effect or no difference.
- You calculate a p-value, which represents the probability of observing the data if H0H_0H0 is true.
- Compare the p-value to the significance level:
- If p≤αp \leq \alphap≤α, reject H0H_0H0.
- If p>αp > \alphap>α, fail to reject H0H_0H0.
For example, if your p-value is 0.03 and your significance level is 0.05, you would reject the null hypothesis because the p-value is smaller than α\alphaα. This decision is influenced by the chosen significance level, highlighting its importance in hypothesis testing.
Also Read: Bert Girigorie
Is significance level equal to Confidence Coefficient in Confidence Intervals
The confidence coefficient is essential in the context of confidence intervals. A confidence interval provides a range of values within which the true population parameter is likely to lie. The confidence coefficient reflects the probability that this range is accurate.
For instance, if you construct a 95% confidence interval, the confidence coefficient is 0.95, and the corresponding significance level is 0.05. This means there is a 5% chance that the true value lies outside the interval.
To further clarify the relationship, consider this table:
| Significance Level (α\alphaα) | Confidence Coefficient | Confidence Level (%) |
| 0.05 | 0.95 | 95% |
| 0.01 | 0.99 | 99% |
| 0.10 | 0.90 | 90% |
From this table, it is evident that as the significance level decreases, the confidence coefficient increases, leading to greater confidence in your results.
Practical Applications of These Concepts
Understanding whether is significance level equal to confidence coefficient is important for applying these concepts effectively. Both are used in various fields, such as:
- Medical Research: Lower significance levels, like 0.01, are common to minimize the risk of false positives.
- Quality Control: Confidence intervals are used to monitor production processes and ensure consistent quality.
- Business Analytics: Hypothesis tests help companies make data-driven decisions, balancing significance levels with confidence coefficients.
By tailoring the significance level and confidence coefficient to the context, analysts can ensure accurate and reliable results.
Common Misconceptions
One common misconception about is significance level equal to confidence coefficient is that the significance level and confidence coefficient are interchangeable. While they are related, they serve different purposes. The significance level focuses on controlling errors in hypothesis testing, while the confidence coefficient emphasizes the reliability of interval estimates.
Another misunderstanding is that a higher confidence coefficient always leads to better results. While a 99% confidence level provides greater certainty, it also leads to wider confidence intervals, which may be less precise. Choosing the right balance depends on the specific goals of the analysis.
Why This Relationship Matters
The relationship between significance level and confidence coefficient is crucial for interpreting statistical findings. By understanding their connection, you can make informed decisions about your analysis.
For example:
- If you want to minimize the chance of a Type I error, choose a smaller significance level, such as 0.01.
- If you need more precise estimates, consider how the confidence coefficient affects the width of confidence intervals.
These decisions can have a significant impact on the validity and reliability of your results.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the relationship between significance level and confidence coefficient?
The significance level (α\alphaα) and confidence coefficient are complementary. The confidence coefficient equals 1−α1 – \alpha1−α, meaning a 95% confidence coefficient corresponds to a 5% significance level.
Are significance level and confidence coefficient the same?
No, they are not the same. The significance level controls the risk of a Type I error, while the confidence coefficient measures the reliability of an interval estimate.
Why is confidence coefficient important in statistics?
The confidence coefficient represents the probability that a confidence interval contains the true parameter value, ensuring the reliability of statistical estimates.
How does significance level affect confidence intervals?
A lower significance level results in a higher confidence coefficient and a wider confidence interval, providing more reliable but less precise estimates.
Conclusion
So, is significance level equal to confidence coefficient? The answer is no, but their relationship is essential for sound statistical analysis. The significance level defines the probability of making a Type I error, while the confidence coefficient reflects the reliability of confidence intervals. Together, they provide a complete framework for hypothesis testing and interval estimation.
By understanding how these terms complement each other, you can make informed decisions about your analysis, ensuring accurate and reliable results. Whether you are conducting research, analyzing data, or making business decisions, recognizing the relationship between significance level and confidence coefficient will help you navigate the complexities of statistics with confidence.




